Restoring Function. Embracing Life.
Rotator Cuff Specialist in Singapore
Dr Bryan Wang
Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
Trusted Orthopaedic Surgeon | Fellowship-trained in Canada | With over 20-years of experience
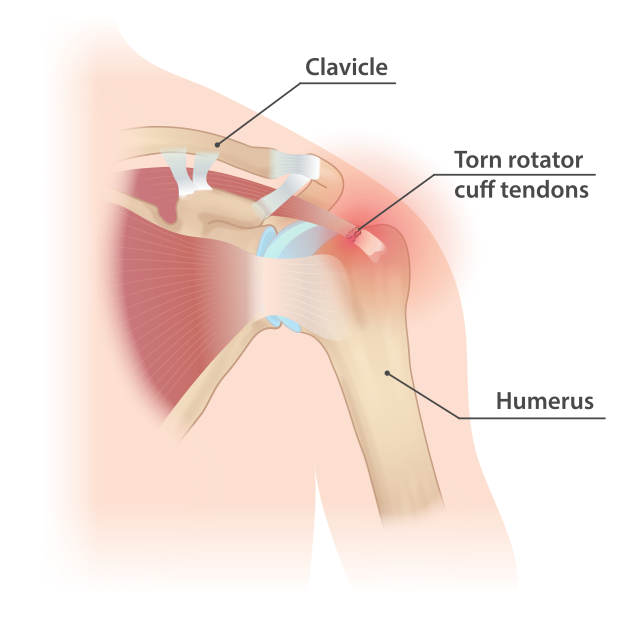
What is Rotator Cuff Injury?
The rotator cuff is a group of 4 muscles which helps to stabilise and move the shoulder joint. Rotator cuff injuries can range from shoulder impingement/tendinitis to partial or complete tears.
Rotator cuff injuries can occur due to degeneration (wear and tear) or trauma (fall/dislocation).
Risk factors for developing rotator cuff injuries include increasing age (due to a reduced blood supply) and repetitive overhead activities (due to impingement from bone spurs).
Occasionally, a rotator cuff tear can also occur from a traumatic injury to the shoulder or a shoulder dislocation.
What are the symptoms?
Patients with rotator cuff injuries may present with the following symptoms:
Shoulder pain - when damaged tendons and muscles cannot support the shoulder joint properly, this will lead to discomfort such as shoulder pain.
Shoulder weakness - especially when lifting or rotating the arm. The rotator cuff muscles helps to stabilise and move the shoulder joint. So when they are injured, you are likely to struggle with these actions.
Difficulty sleeping - on the affected side. The pain from the injury can worsen when you put pressure on your shoulder, such as lying on it. This will make sleeping on the side uncomfortable and even painful.
Popping or Cracking sound - when you move your affected shoulder. This is especially when your injured tendons and muscles rub against the bones in the shoulder joint, causing friction and discomfort.
Difficulty in returning to sports/work - this is often made worse by overhead activities when doing sports or even day to day work.
How to Diagnose?
Clinical assessment will include taking a detailed history and a thorough examination of your shoulder.
Further imaging tests like X-rays, MRI scans and ultrasound scans may occasionally be required.
Rotator Cuff Injury Treatment
What are my Treatment options?
If you have any of the symptoms above, it is advisable to see an orthopaedic specialist for further assessment. The appropriate treatment is decided after assessment and a collaborative discussion based on your needs. They can be broadly divided into conservative (non-surgical) and surgical options.
Rotator Cuff Injury Conservative Treatment
Non-surgical measures will usually be recommended first if you have not had any prior treatment for your rotator cuff injury. These may include a combination or all of the following measures:
Rest: reduce overhead activities to minimise further impingement
Cold packs: to reduce swelling
Medications: anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling
Physiotherapy: to strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve range of motion
Cortisone injection: this may sometimes be required if the pain is persistent
Rotator Cuff Injury Surgical Treatment
If your shoulder pain and weakness is persistent despite all the above measures, surgery may sometimes be required. The appropriate surgical treatment will depend on the nature of the tear (size, duration) as well as your needs (age, functional demands).
The surgery is typically performed in a minimally-invasive fashion (keyhole) and involves re-attaching the tendon to the bone (if reparable) or a superior capsular reconstruction (if not repairable).
Occasionally, a shoulder replacement (reverse shoulder arthroplasty) may be required if shoulder arthritis has already developed.
Who is suitable for Rotator Cuff Repair Surgery
Whether you’re suitable for rotator cuff repair surgery depends on several factors that our orthopaedic surgeon needs to consider. A good candidate for rotator cuff repair surgery is typically someone who has:
1. A Full-Thickness or Large Tear
Complete tears or partial tears that don’t heal with conservative treatment
Tears greater than 3 cm in active individuals
2. Persistent Pain and Weakness
Significant pain that lasts more than 6 months despite physical therapy and medication
Weakness that limits daily activities, such as lifting, reaching, or combing hair
3. An Acute Injury
Sudden injuries from falls, sports, or heavy lifting that cause immediate pain and loss of function
Younger or active individuals are more likely to benefit from early repair to regain full function
4. Failed Non-Surgical Treatments
If physical therapy, rest, medications, and injections don’t provide relief after 3–6 months, our orthopaedic specialist may recommend surgery
5. Good Overall Health
Candidates should be healthy enough for surgery and recovery
Smokers and those with pre-existing medical conditions or health issues may affect your ability to recover from surgery or increase the risk of complications